Blockchain 101: Understanding the Basics
What is blockchain technology? How does blockchain work? What is blockchain used for?
You may find yourself asking these questions at the mere mention of blockchain, and this is completely understandable. Despite its growing prominence, the term remains an enigma to many. However, by gaining a working understanding of blockchain basics, you will be better able to understand the concept and its growing importance in the digital age.
Blockchain Defined
In essence, blockchain is simply a type of database. However, the key difference between blockchain and common databases is the way the data is structured. Unlike standard databases which store data in centralized, relational tables, blockchain is an open, peer-to-peer (P2P) network that favors communal functionality in lieu of a centralized controlling entity.
In blockchain, data is collected into groupings called blocks. Each block has a certain storage capacity so, when it is filled, it is linked to the previously filled block forming a chain of data — hence the name “blockchain.” When additional information is subsequently added, another new block is formed and added to the existing blockchain.
An important characteristic of blockchain is that, as each block is completed, a time stamp is generated. This makes each blockchain a “timeline of data”; differentiating it from standard databases as well.
A Brief History of Blockchain
While blockchain currently commands a lot of attention, its basic characteristics are hardly a new concept. The technology dates back to 1991, when a group of researchers first described the idea of cryptographically securing data in a chain of blocks, time-stamping the chain so it would be impossible to overwrite or tamper with the data. This concept became the subject of scholarly study and experimentation throughout the next decade.
Then, in 2008, a developer under the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto introduced a model that would become the first functional blockchain that went on to be used as the first public ledger for Bitcoin trading. Since this breakthrough, the technology has grown to surpass its cryptocurrency implications alone, introducing new data-oriented possibilities for countless industries. Today, with innovative entities like Ethereum and Ripple leading the charge, blockchain represents a full-fledged paradigm shift for data sharing, storage, and fortification.
How Does Blockchain Work?
At its core, a blockchain allows a network of individuals to share potentially valuable data in a tamper-proof way. The type of data in question often depends on the blockchain’s industry or purpose. For example, a cryptocurrency-based blockchain stores information on crypto transactions, including the trader, recipient, and amount of currency being exchanged.
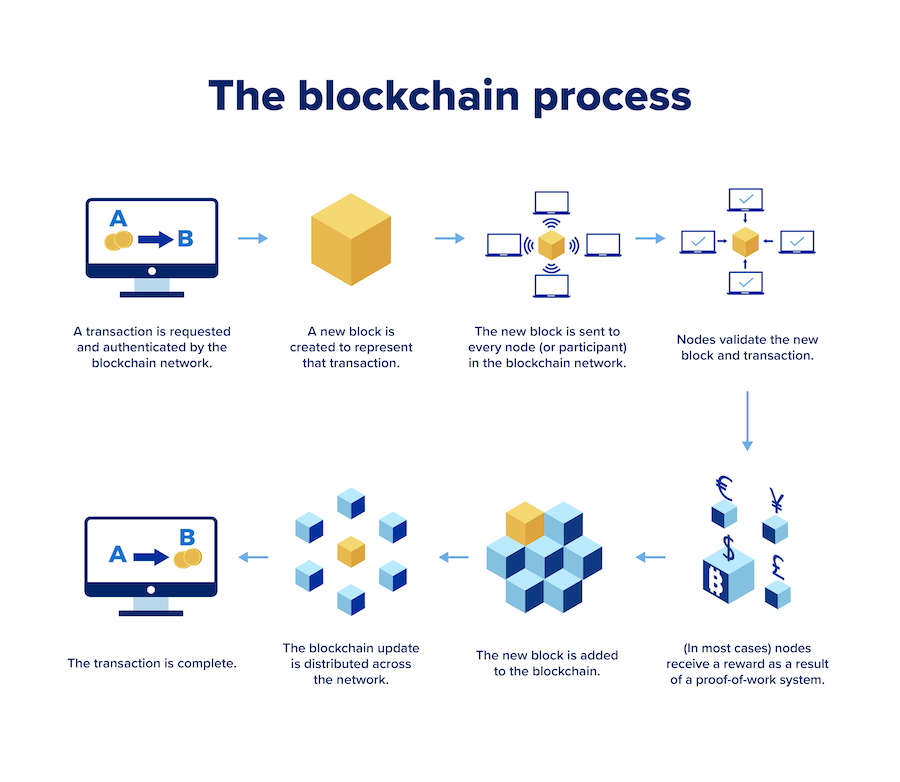
The Blockchain Process
- A transaction is requested and authenticated by the blockchain network.
- A new block is created to represent that transaction.
- The new block is sent to every node (or participant) in the blockchain network.
- Nodes validate the new block and transaction.
- (In most cases) nodes receive a reward as a result of a proof-of-work system.
- The new block is added to the blockchain.
- The blockchain update is distributed across the network.
- The transaction is complete.

 Live Chat
Live Chat