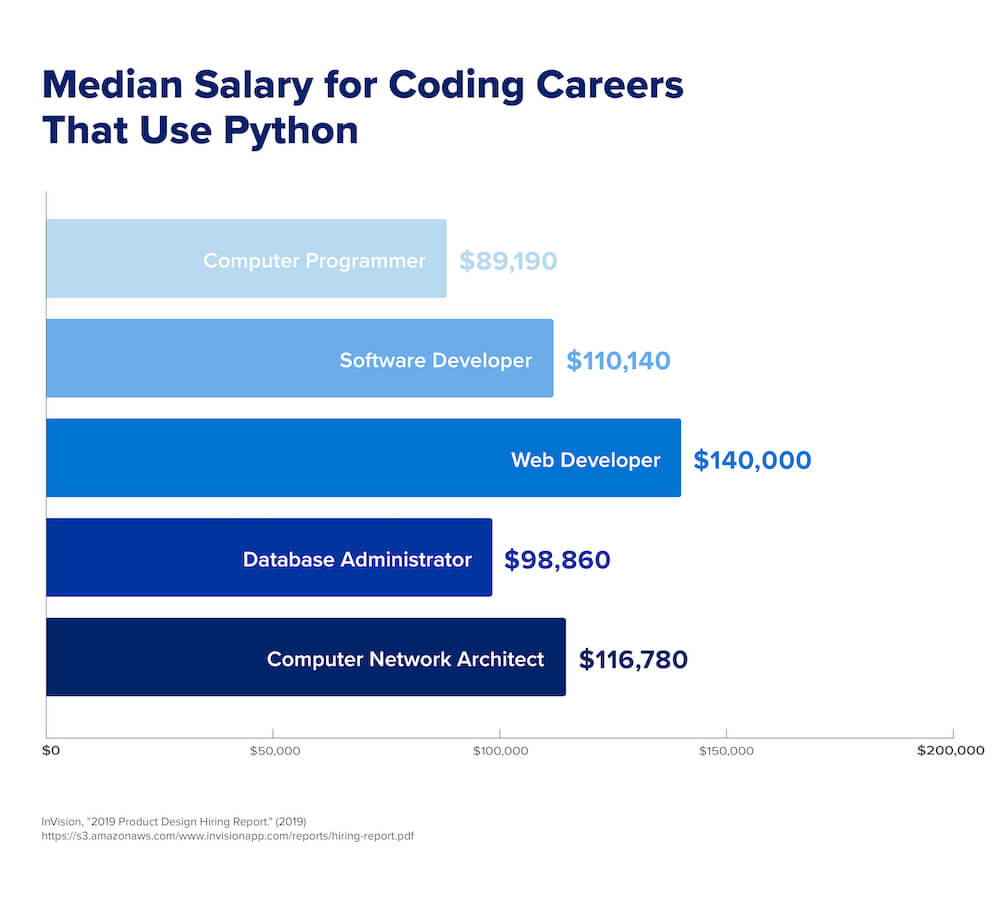
Computer programmers use hundreds of languages to develop software and mobile applications, build websites, and teach computers how to learn. Because it performs all of those functions, Python is among the most popular and important programming languages for aspiring coders and accomplished developers to learn.
Python is a versatile programming language that employers find highly attractive; it can open doors whether you’re looking for a new job, seeking to grow your skills, or hoping to switch industries entirely.
In this article, we’ll explore the Python basics, including answers to the following questions:
- What is Python?
- What can you do with Python?
- What are Python’s basic uses?
- Which careers benefit from a working knowledge of Python?
Read on to learn more about this well-loved programming language.
What is Python?
Python is a multipurpose, high-level, object-oriented programming language — three properties that make it popular with coders and developers. Python is multipurpose because it can be used to create software and apps, design websites, and automate repetitive tasks. Web developers and data scientists like Python for its broad range of companion libraries, accessible syntax, and portability. The library tools and packages help developers shorten and streamline their coding time, and many programmers appreciate that Python requires less time to build projects.
As a high-level language, Python uses an easy-to-read command syntax that it converts to machine code. It also works on the Mac, Windows, and Linux platforms, making it accessible to nearly every programmer.
As an object-oriented language, Python organizes programs into objects and classes that can be reused throughout a project.
Object-Oriented Programming
In object-oriented programming, related variables and functions are grouped into units (or objects). These objects contain data and procedures that determine how they act. In Python, everything is considered an object — and functions are created to determine objects’ actions.
Python Basics: How Does Python Work?
While Python has become an essential language and a very useful skill for data analysts, it requires some basic terminology to get started. If you have a limited programming background, here are a few important terms to know:
Comments
Use a hashtag to leave comments, or notes, to yourself or others explaining elements of your code. In Python, comments are ignored so they are not incorrectly included in the final product.
Keywords
Every programming language relies on certain words to convey meanings or perform specific functions. For example, True and False are used to represent the truth value of an expression within the Python Boolean, one of Python’s built-in data types.
Built-in Data Types
Because variables can store different types of data, it’s important to input the correct data types while programming. Python uses several data types, including numerics, strings, Booleans, lists, and tuples.
Loops
Loops simplify the process of repeating an action for a specific number of steps or until a condition is met. Python presents two types of loops when code needs to be repeated: for and while.
How to Install Python
Python is simple to install; in fact, it might already be installed on your computer. To check, open a command-line window and type “Python.” If the language is installed, a Python interpreter will respond by showing a version number. If not, a link to a free download will likely appear.
If you need to download Python, the language’s free site offers instructions to easily download the latest version for Windows, Mac OS, and Linux.
Here are a few more key related terms to be familiar with as you get started using Python:
Conditionals
Generally speaking, conditional statements facilitate decision-making within a program and perform an action depending on whether a defined condition is true. The primary conditional commands in Python are if and else. Since Python supports common math conditions (e.g., a = 1, b = 2, b > a), the if and else commands deliver instructions based on those conditions. For instance, “print(“b is greater than a”) might follow the conditional “if b > a.” Else might lead to the instruction “print(“b is not greater than a”).
Functions
A function is a block of code that runs when the program commands it to do so. To run the function, programmers simply call it by entering the function’s name into their code. Functions in Python are defined using the “def” keyword, followed by a block of code that defines an action. A program might consist of the line “def coding_function():” which is followed by the function’s steps. To perform the function, a programmer simply enters its name (coding_function).
Operators
In Python, operators perform many tasks: arithmetic functions, assignment of values to variables, comparison of values, combining conditional statements, and more. Common operators include + for adding numbers, * for multiplication, and / for division. Words such as “and,” “or,” “not,” “is,” and “is not” also serve as operators to define and compare variables.
Strings
Strings are sequences of characters that form words or phrases that we can read. In Python, strings are defined in quotation marks, so the line print(“Good morning”) tells the computer to print the string “Good morning.”
Variables
Values are stored in variables. In a simple example, “x = 100,” xis the variable, and 100 is the value. Programmers often name variables more descriptively to provide context to the data they’re referencing. When using Python, programmers don’t need to declare the variable; rather, it’s created very simply: for instance, name = “Mark” assigns the string value “Mark” to the variable “name.”
Mutual Exclusion
Programmers often write programs that use shared files or resources. A mutual exclusion program stops one process from using those files while another process is using them. In Python, programmers can add a mutual exclusion — or “mutex” — to lock one process while another continues to reach its output.
Race Conditions
Python supports multiple processes and multi-threads, but errors can occur. A race condition occurs when two or more threads in a program try to access shared data at the same time; they then try to “race”, which can create instability.
Locks
Locks, like mutual exclusions, can help solve problems caused by race conditions. In Python, locks can be used to synchronize threads so they work together; use the terms acquire and release to move threads between their locked and unlocked states.
Deadlocks
Deadlocks, which can result from flawed implementation of thread locks, are instances programmers want to avoid in Python. They occur when a locked thread isn’t released, which then locks the entire program.
Echo Command
Echo is a common programming command that tells the computer to display an output. In Python, this command is known as print — so the line print(‘Hello’) tells the computer to display the word Hello.
Enhancing With HTTP
Python encourages its community members to introduce new features or provide input on existing features. These Python Enhancement Proposals (or PEPs) go through a lengthy review and approval process but contribute to the sustainability and longevity of Python.
Debugging Tools
Python offers a number of other editing and debugging tools in its library, including pdb, which is accessed with the import pdb instruction.
How to Use Python
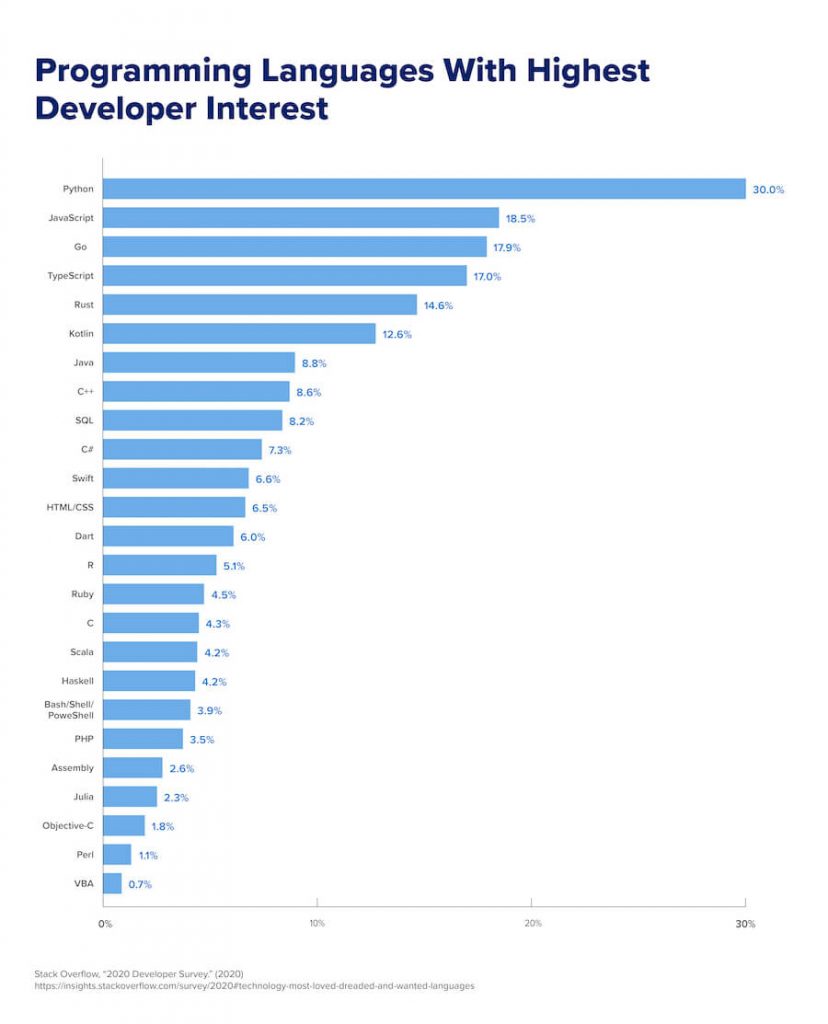
Python consistently ranks among the most in-demand languages because so many programmers use it across a variety of industries. In fact, developers consider Python among their most-loved languages, according to a Stack Overflow survey, and rate it highly on their must-learn lists, according to HackerRank (PDF, 2.4 MB).
 So, what can you do with Python? Here are a few examples.
So, what can you do with Python? Here are a few examples.
Mining Social Media Data
Python users can access a variety of tools to generate insight from data, making the language a favorite for data analysis. For example, Python can be used to write a program that studies Twitter or Facebook data.
Game Design
Python features many game libraries — developers are supported by a series of modules found within the language’s libraries.
Web Development
Django was designed and introduced to support Python. The development framework also contains many of the essential tools for web development, making Python a useful tool for building websites.
Machine Learning
Python has a collection of libraries designed specifically to classify and analyze data, key components of machine learning and artificial intelligence. As a result, Python is considered among the top languages for machine learning.

 Live Chat
Live Chat