When a company needs to build a new product or enhance an existing offering, a product manager can help them understand and represent users’ needs, monitor the market, develop competitive analysis, and define a vision for a product. Product managers perform various activities in industries like healthcare, human resources, and technology, advocating for users by building the best product possible. This organizational function guides all steps of the product life cycle, from development to market positioning and price setting.
Product managers play a key role in creating better products that revolutionize the market or improve customer access. With increasing competition and the growing number of savvy consumers, product managers are in demand in a variety of fields, and product management can provide a strong path to an excellent future career. Columbia Engineering Product Management Boot Camp can help you learn the skills needed to be a professional product manager, uncover the product management roles you’ll be able to qualify for, and provide career support to get employer attention.
What Does a Product Manager Do?
Regardless of their industry, product managers will likely need to conduct several common tasks. These may include driving strategic development, market launches, and market changes for a company’s products. It’s easy to think of project managers when product management is mentioned, but make sure you know the difference between project management and product management before you take the next step in your skills development.
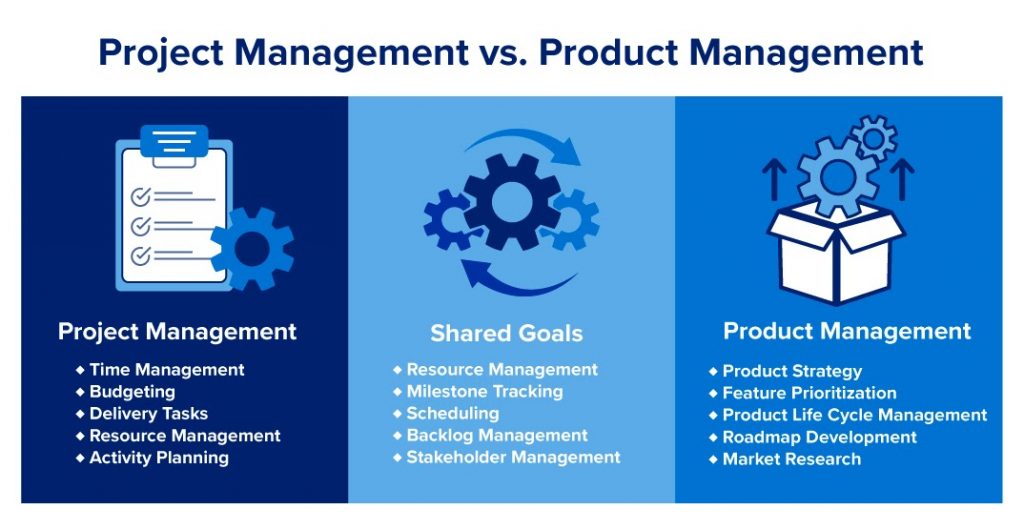
While project management focuses on bringing a project from beginning to completion, product management involves the ongoing vision of a company’s brands and products. The product management definition includes many strategic and tactical responsibilities for complete oversight of a company’s product pipeline and offerings.

 Live Chat
Live Chat